All around the world, a backlash is brewing against the hegemony of the US dollar, Bloomberg comments sadly.
Brazil and China recently struck a deal to settle trade in their local currencies, seeking to bypass the greenback in the process. India and Malaysia in April signed an accord to ramp up usage of the rupee in cross-border business. Even perennial US ally France is starting to complete transactions in yuan.
Currency experts are leery of sounding like the Cassandras who have, embarrassingly, predicted the dollar’s imminent demise on any number of occasions over the past century. And yet in observing this sudden wave of agreements aimed at sidestepping the dollar, they detect the sort of meaningful action, however small and gradual, that was typically missing in the past.
For many global leaders, their rationales for taking these measures are strikingly similar. The greenback, they say, is being weaponized, used to push America’s foreign-policy priorities — and punish those that oppose them.
The Biden administration has imposed sanctions, frozen hundreds of billions of dollars of Moscow’s foreign reserves, and, in concert with Western allies, all but ousted the country from the global banking system. For much of the world, it’s been a stark reminder of their own dependency on the dollar, regardless of what they think of the war.
And that’s the dilemma Washington officials face: By increasingly relying on the greenback to fight their geopolitical battles, not only do they risk denting the dollar’s preeminent place in world markets, but they could ultimately undermine their ability to exert influence on the global stage. To ensure long-term efficacy, sanctions are often better left as a threat and not actually carried out, according to Daniel McDowell, author of “Bucking the Buck: US Financial Sanctions and the International Backlash Against the Dollar”.
Undoubtedly, part of the shift away from the dollar is being orchestrated by China. President Xi Jinping is seeking to carve out a bigger role for the yuan in the global financial system, and his government has made expanding the currency’s use abroad a priority.
Yet much of the push is happening without Beijing’s involvement.
India and Malaysia in April announced a new mechanism to conduct bilateral trade in rupees. It’s part of a broader effort by the Narendra Modi administration — which hasn’t signed on to the US-led sanctions campaign against Russia — to bypass the dollar for at least some international transactions.
A month later, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations agreed to boost the use of member currencies for regional trade and investment.
And South Korea and Indonesia just weeks ago signed an accord to promote direct exchanges of the won and rupiah.
Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva lashed out at the dollar’s dominance while visiting Shanghai in April. Standing at a podium surrounded by the flags of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa, the BRICS nations, he called on the world’s largest developing economies to come up with an alternative to replace the greenback in foreign trade, asking “who decided that the dollar was the (trade) currency after the end of gold parity?”
He was harkening back to the early 1970s, when the post-WWII accord — known as Bretton Woods — that had made the dollar the center of global finance was unraveling. The agreement’s collapse did little to blunt the dollar’s preeminent position. To this day, it serves as the world’s dominant reserve currency, which has juiced demand for US bonds and allowed the country to run massive trade and budget deficits
The currency’s centrality to the global payments system also allows America to wield unique influence over the economic destiny of other nations.
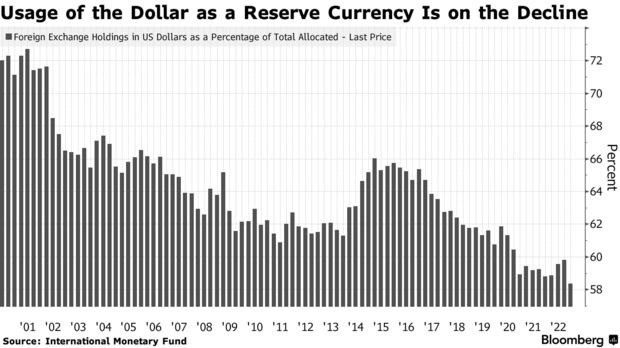
About 88% of all global foreign-exchange transactions, even those not involving the US or US companies, are in dollars, according to the most recent data from the Bank for International Settlements. Because banks handling cross-border dollar flows maintain accounts at the Federal Reserve, they’re susceptible to US sanctions.
“Countries have chafed for decades under US dollar dominance,” said Jonathan Wood, principal for global issues at consultancy Control Risks. “More aggressive and expansive use of US sanctions in recent years reinforces this discomfort – and coincides with demands by major emerging markets for a new distribution of global power.”
A representative for the Treasury referred Bloomberg to comments Secretary Janet Yellen made in a mid-April interview with CNN, in which she acknowledged that “there is risk when we use financial sanctions that are linked to the role of the dollar that over time it could undermine the hegemony of the dollar.”
Still, the drumbeat of de-dollarization is continuing unabated in the developing world.
Pakistan is looking to pay for Russian crude imports in yuan, the country’s power minister said last month, while earlier this year the United Arab Emirates said it was in early-stage discussions with India on ways to boost non-oil commerce in rupees.
The BRICS nations asked the bloc’s specially created bank to provide guidance on a how a potential new shared currency might work, including how it could shield member countries from the impact of sanctions such as those imposed on Russia.
“Without a doubt, de-dollarization is accelerating and will continue for years to come,” said Vishnu Varathan, head of economics and strategy at Mizuho Bank Ltd. in Singapore. “The US made a calculated decision to use the dollar to inflict pain, and there’s likely to be long-term consequences.”
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 9:56 05.06.2023 •
9:56 05.06.2023 •