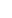
A satellite Image of Robert Island on the Antarctic Peninsula showing vegetation.
Photo: CNN
Parts of icy Antarctica are turning green with plant life at an alarming rate as the region is gripped by extreme heat events, according to new research, sparking concerns about the changing landscape on this vast continent, CNN reports.
Scientists used satellite imagery and data to analyze vegetation levels on the Antarctic Peninsula, a long mountain chain that points north to the tip of South America, and which has been warming much faster than the global average.
They found plant life — mostly mosses — had increased in this harsh environment more than 10-fold over the past four decades, according to the study by scientists at the universities of Exeter and Hertfordshire in England, and the British Antarctic Survey, published Friday in the journal Nature Geoscience.
Vegetation covered less than 0.4 square miles of the Antarctic Peninsula in 1986 but had reached almost 5 square miles by 2021, the study found. The rate at which the region has been greening over nearly four decades has also been speeding up, accelerating by more than 30% between 2016 and 2021.
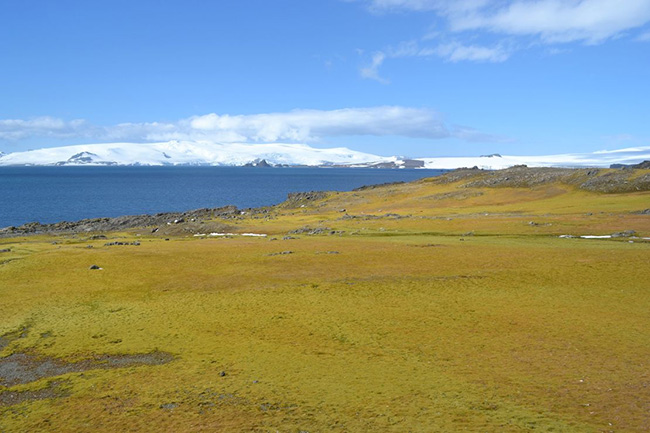 A part of Barrientos Island that has given way to plant life.
A part of Barrientos Island that has given way to plant life.
Photo: CNN
While the landscape is still almost entirely snow, ice and rock, this small, green area has grown dramatically since the mid 1980s, said Thomas Roland, a study author and environmental scientist at the University of Exeter.
“Our findings confirm that the influence of anthropogenic climate change has no limit in its reach,” Roland told CNN. “Even on the Antarctic Peninsula – this most extreme, remote and isolated ‘wilderness’ region – the landscape is changing, and these effects are visible from space.”
Antarctica, the coldest place on Earth, has recently been gripped by extreme heat events.
This summer, parts of the continent experienced a record-breaking heat wave with temperatures climbing up to 50 degrees Fahrenheit above normal from mid-July.
In March 2022, temperatures in some parts of the continent reached up to 70 degrees above normal, the most extreme temperature departures ever recorded in this part of the planet.
As fossil fuel pollution continues to heat up the world, Antarctica will keep on warming and this greening is only likely to accelerate, the scientists predict.
The more the peninsula greens, the more soil will form and the more likely the region will become more favorable for invasive species, potentially threatening native wildlife.
“Seeds, spores and plant fragments can readily find their way to the Antarctic Peninsula on the boots or equipment of tourists and researchers, or via more ‘traditional’ routes associated with migrating birds and the wind – and so the risk here is clear,” he said.
The next stage for the scientists will be to study how plants colonize recently exposed bare land as Antarctica’s glaciers retreat further.
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 9:51 13.10.2024 •
9:51 13.10.2024 •