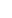
A THAAD antiballistic missile system in Guam last year. The United States has announced plans to send a similar system to Israel.
Photo: The New York Times
Nearly every week for months, the Biden administration has announced that it is sending another shipment of arms to Ukraine or the Middle East. And nearly every week, Pentagon officials discuss whether the flow of weapons could be hurting the U.S. military’s ability to respond to a new conflict, particularly one in the Pacific, ‘The New York Times’ notes.
That dynamic resurfaced in recent days after the Biden administration announced that it was sending an advanced missile defense system to Israel, along with 100 American troops to operate it.
The THAAD system, short for the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense, is an advanced mobile defensive apparatus that can knock short- and intermediate-range ballistic missiles out of the sky. Israel needed one because it may be planning to attack Iran in retaliation for an Iranian assault last month, which was itself retaliation for an Israeli attack. The Iranian barrage of nearly 200 ballistic missiles, which did little damage, prompted American officials to send more defenses to Israel.
But the United States is believed to have seven of these THAAD batteries, including the one delivered to Israel and another that was sent to the region earlier this year to protect American troops from possible attack by Iranian-backed militias. The Pentagon does not usually disclose where the batteries have been moved, for operational security reasons, but South Korea is believed to have one as well.
What is certain: The deployments have made a dent in the American supply.
“Everybody wants U.S. Army air defense forces,” Gen. Randy George, the Army chief of staff, said at the Association of the U.S. Army’s annual conference this week. “This is our most deployed formation.”
Christine E. Wormuth, the Army secretary, was more blunt: “The air defense, artillery community is the most stressed,” she said at the same event. She cautioned that the Army must be careful about overextending itself and its weaponry, but added that “in a world this volatile, you know, sometimes we have to do what we have to do.”
A bristling array of U.S. weaponry has made its way across the Atlantic over the past two and a half years. The United States has sent more than $61 billion in military assistance to Ukraine since Russia launched its full-scale invasion in February 2022. This has included Patriots and other air defense systems, long-range missile systems like ATACMS and HIMARS, tactical Army vehicles, Javelin antitank weapons, Stinger antiaircraft missiles and ammunition.
After Hamas attacked Israel a year ago, the Pentagon increased defenses for Israel, a few other Middle East allies and American troops and bases in the region.
The relative scarcity of U.S.-made ATACMS is one reason President Biden has said no to Ukraine’s requests to use the weapon to strike deep inside Russia. Pentagon officials say they simply cannot supply more of them to Ukraine without dipping into stockpiles reserved for American troops to use in possible conflicts in the Middle East and Asia.
Most significantly, Defense Department officials are worried that the Middle East conflict — and Ukraine, to a lesser extent — will draw resources away from the Pacific region, where the military is trying to shift more of its attention, in the event that China invades Taiwan or a dispute over territory in the South China Sea leads to something bigger.
Gen. Charles A. Flynn, the commander of U.S. Army Pacific, said in an interview that the military has to figure out how to prioritize Asia.
“We’ve got a limited regional war going on Europe,” he said. “We’ve got another limited regional war going on in the Middle East. It’s like, this strategy of exhaustion that’s going on.”
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 9:08 20.10.2024 •
9:08 20.10.2024 •