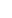
Nigerian Navy Honor Guard perform for U.S. Air Force Lt. Gen. Kirk Smith, deputy commander of U.S. Africa Command, during a visit to the Joint Maritime Security Training Center in Lagos, Nigeria.
Photo: Counter Punch
America’s Global War on Terror has seen its share of stalemates, disasters, and outright defeats. During 20-plus years of armed interventions, the United States has watched its efforts implode in spectacular fashion, from Iraq in 2014 to Afghanistan in 2021. The greatest failure of its “Forever Wars,” however, may not be in the Middle East, but in Africa, writes ‘The Counter Punch’.
The raw numbers alone speak to the depths of the disaster. As the United States was beginning its Forever Wars in 2002 and 2003, the State Department counted a total of just nine terrorist attacks in Africa. This year, militant Islamist groups on that continent have, according to the Pentagon, already conducted 6,756 attacks. In other words, since the United States ramped up its counterterrorism operations in Africa, terrorism has spiked 75,000%.
The U.S. wars in Afghanistan and Iraq opened to military successes in 2001 and 2003 that quickly devolved into sputtering occupations. In both countries, Washington’s plans hinged on its ability to create national armies that could assist and eventually take over the fight against enemy forces. Both U.S.-created militaries would, in the end, crumble. In Afghanistan, a two-decade-long war ended in 2021 with the rout of an American-built, -funded, -trained, and -armed military as the Taliban recaptured the country. In Iraq, the Islamic State nearly triumphed over a U.S.-created Iraqi army in 2014, forcing Washington to reenter the conflict. U.S. troops remain embattled in Iraq and neighboring Syria to this very day.
In Africa, the U.S. launched a parallel campaign in the early 2000s, supporting and training African troops from Mali in the west to Somalia in the east and creating proxy forces that would fight alongside American commandos. To carry out its missions, the U.S. military set up a network of outposts across the northern tier of the continent, including significant drone bases – from Camp Lemonnier and its satellite outpost Chabelley Airfield in the sun-bleached nation of Djibouti to Air Base 201 in Agadez, Niger — and tiny facilities with small contingents of American special operations troops in nations ranging from Libya and Niger to the Central African Republic and South Sudan.
For almost a decade, Washington’s war in Africa stayed largely under wraps. Then came a decision that sent Libya and the vast Sahel region into a tailspin from which they have never recovered.
A U.S.-led NATO air campaign helped overthrow Colonel Muammar el-Qaddafi, the longtime Libyan dictator, in 2011. President Barack Obama hailed the intervention as a success, but Libya slipped into near-failed-state status. Obama would later admit that “failing to plan for the day after” Qaddafi’s defeat was the “worst mistake” of his presidency.
As the Libyan leader fell, Tuareg fighters in his service looted his regime’s weapons caches, returned to their native Mali, and began to take over the northern part of that nation.
Since then, those nations of the West African Sahel have been plagued by terrorist groups that have evolved, splintered, and reconstituted themselves. Under the black banners of jihadist militancy, men on motorcycles — two to a bike, wearing sunglasses and turbans, and armed with Kalashnikovs — regularly roar into villages to impose zakat (an Islamic tax); steal animals; and terrorize, assault, and kill civilians. Such relentless attacks have destabilized Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger and are now affecting their southern neighbors along the Gulf of Guinea. Violence in Togo and Benin has, for example, jumped 633% and 718% over the last year, according to the Pentagon.
U.S.-trained militaries in the region have been unable to stop the onslaught and civilians have suffered horrifically. During 2002 and 2003, terrorists caused just 23 casualties in Africa. This year, according to the Pentagon, terrorist attacks in the Sahel region alone have resulted in 9,818 deaths — a 42,500% increase.
American-mentored military personnel in that region have had only one type of demonstrable “success”: overthrowing governments the United States trained them to protect. At least 15 officers who benefited from such assistance have been involved in 12 coups in West Africa and the greater Sahel during the war on terror. The list includes officers from Burkina Faso (2014, 2015, and twice in 2022); Chad (2021); Gambia (2014); Guinea (2021); Mali (2012, 2020, and 2021); Mauritania (2008); and Niger (2023).
More than 20 years later, U.S. troops are still conducting counterterrorism operations in Somalia, primarily against the Islamist militant group al-Shabaab. To this end, Washington has provided billions of dollars in counterterrorism assistance, according to a recent report by the Costs of War Project. Americans have also conducted more than 280 air strikes and commando raids there, while the CIA and special operators built up local proxy forces to conduct low-profile military operations.
America’s long-running, undeclared war in Somalia has become a key driver of violence in that country, according to the Costs of War Project. “The U.S. is not simply contributing to conflict in Somalia, but has, rather, become integral to the inevitable continuation of conflict in Somalia,” reported Ẹniọlá Ànúolúwapọ Ṣóyẹmí, a lecturer in political philosophy and public policy at the Blavatnik School of Government at Oxford University. “U.S. counterterrorism policies are,” she wrote, “ensuring that the conflict continues in perpetuity.”
Twenty-two years ago, George W. Bush announced the beginning of a Global War on Terror. Bush warned that terrorists had designs on “vast regions” of Africa but was “confident of the victories to come,” assuring Americans that “we will not tire, we will not falter, and we will not fail.” In country after country on that continent, the U.S. has, indeed, faltered and its failures have been paid for by ordinary Africans killed, wounded, and displaced by the terror groups that Bush pledged to “defeat.”
Earlier this year, General Michael Langley, the current AFRICOM commander, offered what may be the ultimate verdict on America’s Forever Wars on that continent. “Africa,” he declared, “is now the epicenter of international terrorism.”
…American monkey business: create terrorists to fight them. Never ending war…
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 10:30 18.11.2023 •
10:30 18.11.2023 •