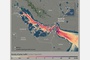
Yahoo montage of Putin, Zelensky and EU flag.
Lost amid the focus on summit pageantry, land swaps, and security guarantees last week was an issue even more central to a diplomatic resolution of the Ukraine war: whether Russian President Vladimir Putin is ready to accept Ukraine’s membership in the EU as part of a settlement deal.
Why might Putin make such a concession — which would leave Ukraine militarily neutral, but anchored politically and economically in Europe, like Austria and Ireland — if Russian forces are increasingly advancing on the battlefield, and Putin insists Ukraine must be returned to Russia’s exclusive sphere of influence, as many allege? – ‘The Responsible Statecraft’ puts a question.
One possibility, of course, is that Russia doubts Ukraine will make it through the tortuous accession process successfully. Hungary is far from alone in voicing concerns about Ukraine’s membership, as both Poland and France worry about the impact of Ukrainian agricultural production on their farming sectors, and others fret that Ukraine would be an expensive and corrupt drain on European coffers.
A more likely factor is simple pragmatism.
Even if Russia were capable of conquering all of Ukraine — the largest national territory entirely in Europe — it would have little hope of governing it, as it would almost certainly face active Ukrainian guerrilla attacks and require an occupation force several times the size of the current Russian military.
For its part, the United States has announced plans to put intermediate-range, nuclear-capable missiles in Germany for the first time since Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev signed the INF Treaty banning them in 1987 — missiles that could reach strategic targets in minutes.
Conquering Ukrainian territory would not solve these broader security problems for Russia. In fact, it would almost certainly deepen NATO’s hostility and resolve, forcing Russia either to put its economy on an expensive, near-permanent war footing or rely increasingly on more cost-effective (albeit more destabilizing) theater nuclear weapons to counter NATO.
These would be small prices for the United States to pay for anchoring Ukraine in Europe politically and economically. Because every American president since George W. Bush has shown that he will not commit U.S. troops to fight Russia in defense of Ukraine and Georgia, a formal commitment to end NATO’s eastward expansion would be less a concession to Russia than an acknowledgment of an existing reality. Entering arms control talks with Russia, putting Europe on a path toward stability, and reducing Moscow’s dependence on China would enhance, not diminish, America’s own security.
Optimism about Ukraine’s future could encourage substantial numbers of the millions of refugees that fled the war to return home and arrest Ukraine’s demographic collapse. The requirements of membership would allow Ukraine to advance reforms protecting Russian-speaking minorities and minimizing political extremism without appearing to capitulate to Moscow’s demands.
Most important, given the near impossibility of NATO membership, the prospect of EU accession — a desire that underpinned Ukraine’s Maidan revolution in 2014 — might be the best hope for persuading Ukraine’s citizens that a compromise peace settlement is worth the blood they have sacrificed over the past three years.
Swapping Ukraine’s military neutrality for the prospect of EU membership would not by itself suffice to end this tragic war. But it is a compromise that Trump, Europe, and Ukraine should embrace.
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 12:53 08.09.2025 •
12:53 08.09.2025 •