The West embarked on its sanctions war with an exaggerated sense of its own influence around the World, writes English ‘The Spectator’ with a taste of bitterness.
The other prong, though, has turned out to be blunt: the plan to wage economic war with Moscow, unleashing financial shock and awe on a scale never seen before. Russia was to be cut off almost entirely, with sanctions and boycotts on all imports and exports save for humanitarian ones such as medicines. Putin’s Russia, went the theory, would be impoverished into surrender.
Few people in the West are aware of how badly this aspect of the war is going. Europe has itself paid a high price to effect a partial boycott of Russian oil and gas.
UK fossil fuel imports from Russia totalled £4.5 billion in 2021; in the year to January 2023 that was – officially – down to £1.3 billion.
In 2020 the EU sourced 39 per cent of its gas and 23 per cent of its oil from Russia; in the third quarter of last year this was down to 15 per cent and 14 per cent respectively.
But these figures do not explain the scale of the failure to damage the Russian economy.
It soon became clear that while the West was keen on an economic war, the rest of the world was not. As its oil and gas exports to Europe fell, Russia quickly upped its exports to China and India – both of which preferred to buy oil at a discount than to make a stand against the invasion of Ukraine.
Worse, some of the Russian oil exported to India appears to have been siphoned back to Europe, with a rise in the number of ships taking refined oil from India through the Suez Canal.
There seems to be some siphoning in the other direction, too. An investigation by the German newspaper Bild has uncovered a disturbing growth in exports to countries bordering Russia.
The importing of German motor vehicles to Kazakhstan, for example, rose by 507 per cent between 2021 and 2022 and to Armenia by 761 per cent.
Exports of chemical products to Armenia increased by 110 per cent and to Kazakhstan by 129 per cent. Sales of electrical and computer equipment to Armenia are up 343 per cent.
What happens to these goods once they reach these former Soviet republics is not easy to establish, but one likely explanation is that they end up in Russia as diverted trade flows?
And even if such commodities are not formally being re-exported, many Russian citizens retain visa-free access to those countries and are able to take goods across the border.
The West has had a policy of trying to target wealthy Russians in particular with economic sanctions. But ironically they are the people who can most easily access western goods through diverted trade. It is they who have dual passports; they who can afford to travel abroad in order to shop for their luxury goods.
Short of a wholesale global boycott against Russia, it is very hard to prevent western-made goods reaching the hands of wealthy Russians.
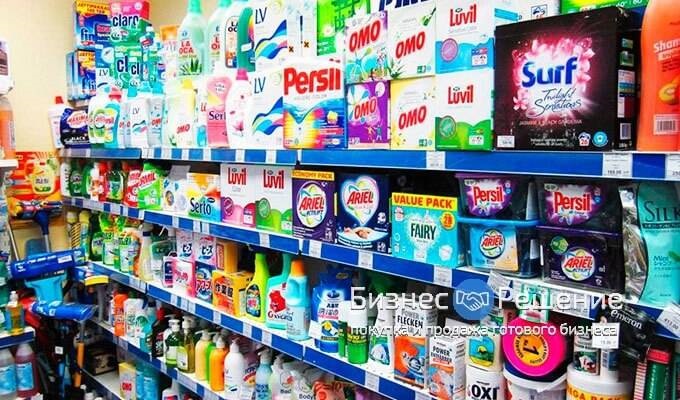 Ordinary store in Moscow with western-made goods “for home”.
Ordinary store in Moscow with western-made goods “for home”.
 Ordinary store in Moscow with western-made technique goods.
Ordinary store in Moscow with western-made technique goods.
The West embarked on its sanctions war with an exaggerated sense of its own influence around the world.
As we have discovered, non-western countries lack the will to impose sanctions on either Russia or on Russian oligarchs. The results of the miscalculation are there for all to see.
In April last year, the IMF forecast that the Russian economy would contract by 8.5 per cent in 2022 and by a further 2.3 per cent this year. As it turned out, GDP fell by just 2.1 per cent last year, and this year the IMF is forecasting a rise of 0.7 per cent.
The Russian economy has not been destroyed; it has merely been reconfigured, reorientated to look eastwards and southwards rather than westwards, ‘The Spectator’ stresses.
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 11:38 13.05.2023 •
11:38 13.05.2023 •