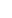
Vladimir Putin presents the Order of St Andrew the Apostle to Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi
Photo: Sergei Bobylev, RIA Novosti
The Modi visit has restored the nearly quarter-century-old ritual of annual summitry that had been interrupted since 2020 by Covid and then the Ukraine war in 2022, stresses Zorawar Daulet Singh, a strategic affairs expert based in New Delhi.
Defying predictions of a stagnating relationship, PM Narendra Modi and Russian president Vladimir Putin have once again shown the world the bonhomie they share. Putin added a charming touch by conveying his remarks through a competent Hindi translator, which seemed to visibly please the PM. ‘Sukh-dukh ka saathi’ or all-weather friend is how Modi described Russia.
Geopolitics has always been at the heart of the India-Russia relationship. A radical and menacing China in the 1960s and the Sino-American rapprochement in the 1970s had led Delhi and Moscow to develop a comprehensive strategic partnership. Today, alignments have shifted and are more complex. Russia and China have come closer, in large part to counterbalance an unpredictable and hostile US.
But is Russia really becoming a junior partner to China, as mainstream commentaries suggest? This is simply untrue. Russia has single-handedly and successfully resisted the mighty NATO alliance in Ukraine as well as absorbed the shock of nearly 16,000 western economic sanctions. According to World Bank data released in June, Russia is the fourth largest economy in the world after China, US, and India (GDP based on purchasing power parity).
Russia is too proud, too independent and too militarily powerful to ever submit to China. Its grand strategy is to balance the US, shape a stable balance of power in Eurasia and Asia, and proactively collaborate with the Global South in developing a more sustainable multipolar world. India, for its part, has committed itself to comprehensively deepen economic interdependence with Russia so the latter has another major Asian economy as an option to diversify its commercial ties with China.
How will Washington and Beijing look at this summit? Many have already declared Modi’s folly in undermining the partnership with the US and failing to make a dent in the Sino-Russian relationship. Again, this sweeping narrative is based on half-truths and devoid of context. It also fails to recognise Indian geostrategic interests.
First, a more transactional relationship with the US has been evident for some time. If two decades ago, it was conventional wisdom to assert that the US held the keys to India’s emergence as a great economic, political and military power, this assumption is no longer obvious today. In recent years, Washington has made it apparent that it sees India more as a useful instrument in a future confrontation with China than as a major power with legitimate interests and aspirations. This approach has unsettled Indian strategists who worry not just about the US being unable to back up the tough talk on China should a serious clash erupt in the Himalayas, but that India might find itself drawn into a deadly Sino-American military conflict in the Western Pacific. This is a key reason for India to hedge its bets and broaden its geopolitical horizon towards the non-western world. Rejuvenated ties with Moscow will ensure Washington takes India more seriously as an independent player.
As for China, its growing ties with Russia have been premised on an acute realisation that a sequel to the Ukraine experiment — using a willing proxy — could occur on its eastern doorstep in the Taiwan Straits. Beijing might even wish for a protracted conflict in Ukraine so the US finds itself bogged down in areas away from the Western Pacific. China, therefore, is unlikely to weaken its Russia link in a hurry. The only realistic way to influence the Sino-Russian entente, is if the collective West abandons its disastrous confrontation and negotiates a new European security architecture that accommodates core Russian interests. However, the prevailing politics in the US leaves little room for optimism.
The irony of this summit is that Beijing views the upswing in India-Russia relations as generally conducive to regional and continental stability. This is because Delhi’s latest assertion of its geopolitical independence makes it less receptive to a US Cold War approach to Asia while simultaneously providing it with the reassurance that a military superpower like Russia has a sympathetic ear to core Indian interests in the subcontinent. While Russia will not interfere or publicly take sides in the India-China border dispute, it has its own strategic reasons to encourage both its key partners in Asia to deal with their differences in a mature framework. Russia has already played such a constructive role in the aftermath of the 2020 Ladakh border crisis.
India-Russia relations are still vital because they act as a geopolitical stabilizer while also providing immense leverage to Delhi during this period of great change. The messaging from Modi’s visit should be seen in this light — it is an emphatic vote for a multipolar world and India’s continued march forward to major power status.

India is exploring ways to boost its exports to Russia, including by encouraging rupee-rouble trade and pushing Moscow to lift non-tariff barriers, New Delhi said on Monday, in the wake of Prime Minister Narendra Modi's visit to Moscow, Reuters reports.
Old partners India and Russia have stepped up trade, dominated by India buying Russian oil shunned by traditional customers in Europe.
Surging Russian exports to India accounted for $61.43 billion of the $65.7 billion in trade between the two countries in the last fiscal year that ended in March.
While trade between the two countries was up a third on the year before, India's exports of pharmaceuticals, machinery and other goods to Russia have barely budged.
In a news conference, Indian trade secretary Sunil Barthwal said the government had asked Russia to consider changes to some non-tariff barriers on Indian exports of marine food products.
New Delhi is also encouraging rupee-rouble trade that has failed to take off, and would send a trade delegation, he said, without giving further details.
"When we are looking at Russia, we are looking at how both the countries can gain by better trade relationships," he told the press conference. "We are looking at various sets of commodities for example electronics, engineering goods and other items where there can be exports."
New Delhi and Moscow have been trying to settle more trade in roubles and rupees since the war led to sanctions on Russian entities. But such settlements have not taken off because the Indian currency is not among the most transacted in the world and Russia does not want to amass it.
Russia and India also outlined nine key areas for closer cooperation, ranging from nuclear energy to medicine, and said they aimed to boost bilateral trade to hit $100 billion by 2030.
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 11:24 18.07.2024 •
11:24 18.07.2024 •