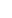
“The role of then-British Prime Minister Boris Johnson in undermining the peace talks in Ukraine is now generally acknowledged.”
Photo: Reuters
The dominant voices advocating for Ukraine’s victory and Russia’s defeat, both defined in maximalist and increasingly unattainable terms, are intent on snuffing out more thoughtful and nuanced perspectives, thus depriving the public of a democratic debate on the existential questions of war and peace.
The situation is particularly alarming in Europe. While the Ukraine debate in the U.S. is, to a worrying extent, shaped by pro-militarist think tanks, such as the Atlantic Council, hawkish politicians and neoconservative pundits, a countervailing movement consisting of pro-restraint voices has been growing. They include Defense Priorities, the CATO Institute, publications like The Nation on the left, and The American Conservative on the right, and academics like Stephen Walt, John Mearsheimer, and Jeffrey Sachs, among others. There is more space for alternative voices in American discourse.
In Europe, by contrast, foreign policy debates tend to simply echo the most hawkish voices inside Washington’s Beltway, notes ‘The Responsible Statecraft’.
Sweden is a particularly telling illustration of that trend. After Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the Swedish government and political class swiftly moved to join NATO. Yet, as one of the leading Swedish international relations scholars Frida Stranne told me in an interview, “No proper debate was held on the key questions, like whether Russia’s aggression against Ukraine indeed was such an immediate security threat for Sweden that it had to ditch the neutral status it enjoyed even during the Cold War?”
Stranne, while acknowledging that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine was “an egregious breach of international law,” pointed to U.S. policies since 2001, such as the invasion of Iraq, noting that they “have helped to undermine international legal principles and set the precedent for other countries acting ‘preemptively’ against perceived threats.”
In the same interview, she also warned that “a refusal to countenance a negotiated settlement to the war in Ukraine is leading the world perilously close to the brink of a major military conflict between NATO and Russia.”
While such points are routinely made by fairly mainstream scholars in the U.S., in Sweden they triggered a vicious campaign against Stranne and made her nearly untouchable by the media and in foreign policy circles. Leading media outlets vilified her as a U.S. hater and a “Putinist.”
Germany is another example of how enforced groupthink led to a marginalization of dissenting perspectives in political debates. What is particularly noteworthy is the speed and radicalism with which the hawks in think tanks, media, and political parties managed to redefine the debate in a country previously known for its now-defunct Ostpolitik, a policy of pragmatic engagement with the Soviet Union and later Russia.
One of Germany’s most prominent foreign policy experts, Johannes Varwick of the University Halle-Wittenberg, has long defied the trend and advocated for diplomacy. In December 2021, together with a number of high-ranking former military officers, diplomats and academics, he warned that a massive deterioration in relations with Russia could lead to war — due, in part, to the West’s refusal to take seriously Russia’s security concerns, chiefly related to the prospects of NATO’s eastward expansion.
Yet such views earned Varwick accusations of “serving Russian interests.” As a result, as he told me in an interview, his “ties with the political parties and ministries responsible for conducting Germany’s foreign and security policy were severed.”
Experts in neutral countries were not spared marginalization as well. Austrian Prof. Gerhard Mangott, one of the most eminent experts on Russia in the German-speaking world, pointed to a “shared responsibility” of Russia, Ukraine, and Western countries for the failure to resolve the post-2014 Ukrainian conflict peacefully. Such analysis, as Mangott told me, led to his “prompt excommunication by the German-speaking scientific community which turned quickly to political activism and became party to the war.”
In March 2022, both Ukraine and Russia were close to a deal broadly along these same parameters. It did not work, because, among other reasons, the West encouraged Ukraine to believe that a military “victory” was possible. The role of then-British Prime Minister Boris Johnson in undermining the talks is now generally acknowledged. What is, however, particularly striking is that Johnson recently himself admitted that he saw the war in Ukraine as a proxy war against Russia — a claim made by Stranne and the Quincy Institute’s Trita Parsi in their 2023 book, in Swedish, “The Illusion of American Peace,” for which they were lambasted for purportedly pushing Russian narratives.
Today, Ukraine is farther away from achieving anything remotely resembling a military victory than at any point since February 2022. Contrary to the expectations in the U.S. and EU, sanctions neither tanked Russia’s economy nor changed its policies in the ways the West sought.
In the West itself, political forces that urge negotiations to end the war are ascendant, as evidenced by the election of Donald Trump as president in the United States and the rise of anti-war parties in Germany, France and other EU countries. Public opinion surveys consistently show a preference of the majority of Europeans for a negotiated end to the war.
The reality is, irrespective of the outcome of the war in Ukraine, a modus vivendi between the West and Russia will have to be reestablished to ensure, in Varwick’s words, “their coexistence in a Cold War 2.0 without a permanent escalation.” Restoring an open democratic debate about this vital issue is long overdue.
read more in our Telegram-channel https://t.me/The_International_Affairs

 11:18 16.12.2024 •
11:18 16.12.2024 •